A life cycle analysis is a systematic examination of the potential environmental effects of products or services throughout the course of their whole existence, from conception to disposal. The Life cycle impact assessment includes all important ecosystem & environmental input parameters, for example, minerals, water consumption, land usage etc. that also include air, water, and soil emissions. The emissions include CO2, CO, NO, SO2, etc. To perform the entire life cycle assessment of a process, product or services the international organization for standards provides recommendation based on the standards ISO 14040 and 14044.
Life Cycle assessment Classification
Primarily, there are three pillars. Social, Economical & Environmental.
- Social: principles that promote justice and respect for the rights of the individual.
- Economic: build a reasonable economic system. lowering consumption and consequently costs
- Environmental: safeguard the environment by minimizing threats.
What is Life Cycle Assessment?
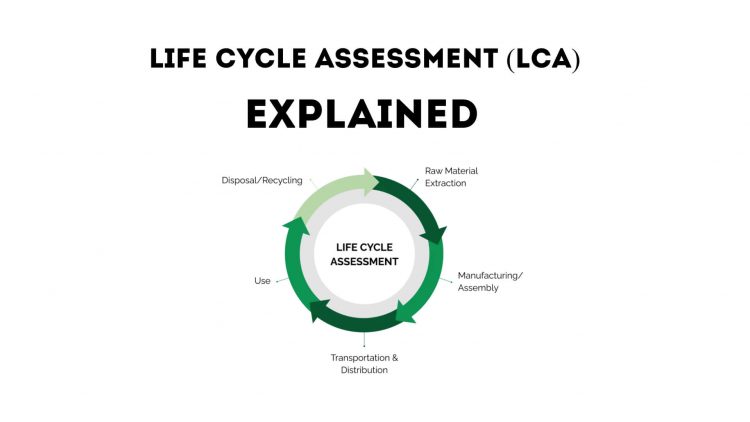
The purpose of the LCA approach is to identify the environmental consequences of a product at several stages of its life, including quarrying the gathering and preparation of raw materials, the production procedure, followed by use/reuse/maintenance, disposal/recycling, and Evaluating the potential environmental consequences of the product at various stages of its life cycle.
The life cycle evaluation process has five stages.
- Quarrying and Raw Material Extraction
- Manufacturing processes
- Packaging and delivery
- Use and retail
- Recycling or disposal of waste
Material Extraction: An examination of where and how the material is extracted. The evaluation of how we obtain materials from nature.
Manufacturing Processes: The activities performed during the product’s manufacturing process. The very first step is the raw material, assessment of raw materials, their airborne emissions, water consumption, energy usage and all relevant inputs and outputs. Similarly all other manufacturing processes inputs including materials, electricity, air emissions etc.
Packaging & Transportation: Product packaging is essential. The material utilized, such as plastic, and its effects and recycling process considered. Similarly, the environmental impacts of transportation are considered.
Usage & Retail: The product’s usage phase begins and concludes its retail life. Evaluating how much energy, water, and other resources were used overall throughout the utilization phase.
Recycling or Waste Disposal: Measuring the final life of a product and its effects. Recycling is the reuse, repair, or remanufacturing of an item. The evaluation of the consequences of waste material, freshwater, and air on the environment and surroundings.
Phases of LCA
There are four phases of LCA:
- Goal & Scope defining
- Analysis of Life Cycle Inventory
- Impact assessment
- Results & discussion Interpretation
Goal & Scope Definition
The procedure of defining the LCA’s objectives and scope guarantees that the analysis is conducted consistently. The LCA represents the life cycle of the product, service, or system.
The objective and scope identify the most crucial, frequently arbitrary judgments. For instance, a detailed explanation of the item and its lifetime, a description of the system’s limits, and the rationale for doing the LCA.
The system boundaries indicate what is included in the evaluation and what is excluded. Small quantities of substances that contributes little to the overall impact can be excluded from the study’s scope.
Inventory Analysis Phase
All ecological outputs and inputs associated with a service or a product are covered in the analysis phase. The LCI is concerned with collecting relevant data and accurately portraying it via inputs and outputs.
Stage of the Life Cycle Impact Assessment
The step of a life cycle analysis (LCA) known as the life cycle impact analysis (LCIA) examines potential environmental effects, the hotspots resulting from environmental resources, identified in the LCI are evaluated. LCIA includes the following procedures:
- Choosing essential impact assessment categories
- Classification: allocating basic flows to the impact or assessment categories
- Modeling or designing the probable impacts utilizing conversion factors to get an indicator for the assessment category.
- Normalization stage (optional): indicating potential implications in relation to a standard
- Selecting or grading the effect indicators
- Evaluation and reporting; relative weighting of effect categories.
Results Interpretation Phase
During the interpretation stage, you verify the validity of your conclusions. The ISO 14044 standard outlines a number of tests to determine if the data and processes you employed support your conclusions.
The Life Cycle impact Assessment and Environmental indicators
According to ISO standard 14040, 3 main protection areas exist. Human health, the natural environment, and natural resources are protected.
The Impacts normally categorized as:
- Atmospheric Impacts
- Resource Depletion
- Eco-toxicity Impacts
Table: Life cycle Impact Assessment Categories
|
No. |
Type |
|
1 |
Climate change – The Global Warming |
|
2 |
Ozone Formation impact |
|
3 |
Terrestrial Acidification |
|
4 |
Particulate matter – Fine Particulate matter formation |
|
5 |
Freshwater eutrophication |
|
6 |
Marine eutrophication |
|
7 |
Terrestrial Ecotoxicity |
|
8 |
Freshwater ecotoxocity |
|
9 |
Marine ecotoxocity |
|
10 |
Land use |
|
11 |
Mineral Resource Scarcity |
|
12 |
Fossil resource scarcity |
|
13 |
Water consumption |
|
14 |
Energy Resources |
|
15 |
Carcinogens |
- The effect on climate the Global rising temperatures or a carbon footprint and other airborne emissions.
- Acidification is the measurement of environmental acidification emissions. The goal is to preserve forests and reduce fish mortality.
- Another effect is the formation of smog, which is an indicator for human health and crop yields.
- Dust and its emissions cause health problems for humans.
- Ozone depletion, measuring the air emitters that impacts the ozone layer’s depletion.
- High levels of micronutrients are responsible for eutrophication, also known as overfertilization. The purpose is to safeguard rivers and lakes.
- Other indicators and effects include the use of Energy, Water, and Land, the limitation of toxic emissions, the preservation of biodiversity, and the reduction of waste and radioactive waste materials.
Benefits / Advantages of LCA:
There are numerous Advantages to Life Cycle Assessment. Performing a life cycle assessment can help improve product advancement. The market demand for sustainable product development is growing.
In the supply chain, suppliers with sustainable products and processes are identified. It enhances the conceptual framework and the design’s effect on the product’s durability.
Some businesses and nations have established environmental standards. To evaluate these needs and requirements, an LCA is performed. The more environmentally conscious and sustainable a product is, the greater its impact on the market. The new products must be more ecologically responsible. LCA provides insights that can enhance marketing and decision approaches.
Cite this Article
| Author: | Scholars Harbor |
| Year: | 2022 |
| Title |
What is Life cycle Assessment (LCA) – LCA Explained |
| Publisher: | Scholars Harbor |
| URL: | https://scholarsharbor.com/what-is-life-cycle-assessment-lca-explained/ |










Discussion about this post