Various items around us are made up of discrete pieces that are then integrated into unique goods. These forms and qualities are unusual in nature. All are created through a series of procedures known as manufacture. Technology is the use of knowledge to provide civilization and its people with what they want or desire. Technology creates items that improve the lives of our society’s citizens. What do these items all have in common? They are entirely fabricated.
Manufacturing is a necessary component that allows technology to exist. Manufacturing’s historical relevance in the evolution of civilization is sometimes underestimated. Human societies that were better at creating things were more successful throughout history.
Making good equipment means making better crafts and weapons; better crafts enabled people to have better lives; and better weaponry enabled them to conquer other civilizations during times of war. To a large extent, the history of civilization is the evolution of people’ ability to create things.
Manufacturing Definition?
The term “manufacture” is derived from the Latin words: manus (hand) and factus (make), and indicates “made by hand.” When the English word “manufacturing” first appeared in 1567 A.D., it accurately characterized the manual processes utilized.
Most modern production is carried out by automated, computer-controlled machinery that is under human supervision. In print, the word “manufacturing” first occurs in 1683. Technically speaking, manufacturing is the employment of physical and chemical processes to alter a starting material’s shape, properties, and/or appearance in order to make parts or products; manufacturing also entails the assembly of several components to create things. Most often, manufacturing is done in a succession of steps.
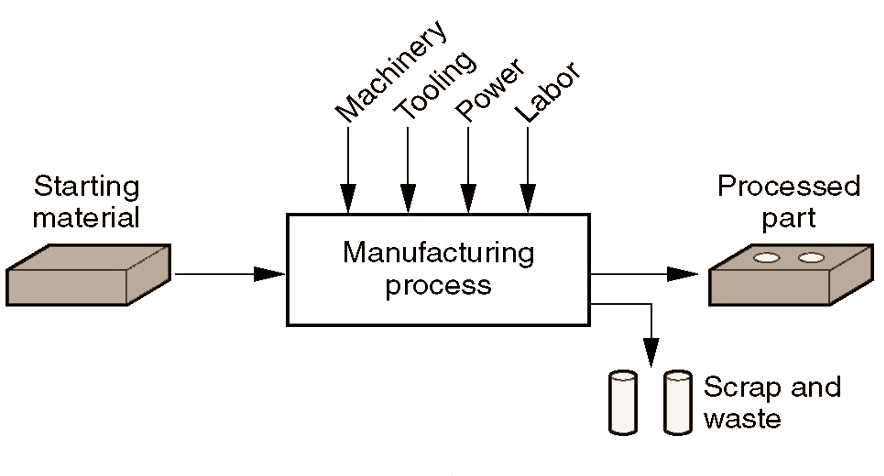
Manufacturing (economically) is the transformation of resources into more valuable objects through one or more processing/assembly procedures. Manufacturing gives value to commodities, such as iron ore being transformed into steel or plastic being changed into complicated shapes such as chairs.
What is Advance Manufacturing?
Advanced manufacturing is the application of science, engineering, and communication technology, as well as high-precision methods and tools in conjunction with a high-performance workforce and innovative commercial or organizational models, to enhance current infrastructure or develop entirely new materials, products, and processes.
Advanced manufacturing is concerned with modern, yet simple to use and cost-effective processes capable of generating geometrically simple and light-weight items with better levels of usefulness, repeatability, environmental friendliness, and durability.
Advanced Manufacturing – Industrial Challenges
Manufacturing must adapt to a number of demands and trends:
- Zero-defect production methods
- Process scalability, flexibility, and adaptation
- Loss of weight
- Sustainability, waste minimization, and energy efficiency
- Cost cutting
- Modern automation
- Man and machine interaction
- Environmental risks to health and safety
- Integrating value chains
- Time to market optimization
- Consistent consumer feedback and rapid implementation of crucial product features
- Risk management, operational management, and total quality management
01: Product Design and Concurrent Engineering:
Product design is an essential task. Typically, the first design stage is where 70 to 80 percent of the cost of product development and production is set. Design and production processes have traditionally been sequential rather than parallel or simultaneous. Sequential may sound sensible, yet it is a huge resource waster.
Concurrent engineering combines product design and production to reduce time, money, and design and engineering adjustments (iterations). CAD/CAM software, virtual prototyping, and other powerful computer-based simulation techniques are crucial components of modern manufacturing for product design.
02: Design for Manufacture, Assembly, Disassembly, and Service
The process of designing a product is integrated with materials, manufacturing techniques, process planning, assembly, testing, and quality control. Designers need to grasp the basics of these activities. When design and assembly activities are combined, it is referred to as “design for manufacturing and assembly” (DFMA).
A product that is simple to assemble is typically also simple to disassemble. Computer assisted expert systems are used to analyze products for production, assembly, disassembly, and simple maintenance.
03: Green and Sustainable Manufacturing
A holistic approach to manufacturing that takes into account social, economic, and environmental factors is known as sustainable manufacturing.
Each year, both consumers and businesses trash a sizable amount of plastic and aluminum. Numerous byproducts (such as slag and scrap), heavy energy use, water and oil use, and air emissions have a negative influence on the environment (greenhouse gases, acid rain, climate change, etc.), which in turn affects human lives and economics.
Recycling initiatives are becoming increasingly significant these days. There are several treaties, conventions, and laws being signed (Kyoto, Paris agreement, SDGs, etc.). Design for reuse and design for the environment examine potential adverse effects of materials, products, and processes on the environment at an early phase of the product creation.
Cite this Article
| Author: | Scholars Harbor |
| Year: | 2022 |
| Title | Manufacturing & Advanced Manufacturing Explained | Advanced Manufacturing Methods |
| Publisher: | Scholars Harbor |
| URL: | https://scholarsharbor.com/manufacturing-advanced-manufacturing-explained-advanced-manufacturing-methods/ |












Discussion about this post