Our daily activities demand energy. A few elements that contribute to an increase in demand for energy include the total population’s sudden increase and continuous individual income growth. There will likely be more than 9.1 billion people on the planet by the year 2040, which means that 2 billion more people would require energy.
Growing power consumption and depleting fossil fuel availability are key issues, together with concerns about the impact of using conventional fossil fuels on people’s health. The usage of green energy is urgently required to replace current conventional fossil fuels. It has been reported that the production of renewable energy has increased globally.
Renewable energy sources, however, are unable to produce reliable, uninterrupted, and continuous power on their own. In recent years, it has become more difficult to promote the utilization of clean power due to the unpredictability and the imbalance between demand and supply. This issue can be resolved by storing excess energy in the fuel cell and utilizing it during times of peak demand.
Working Principle of Fuel Cell
Fuel cells use electrochemical reactions, which are really just reversed electrolysis reactions, to produce energy and heat. This process takes place when oxygen and hydrogen combine to create water. The cell reaction can be expressed as follows.
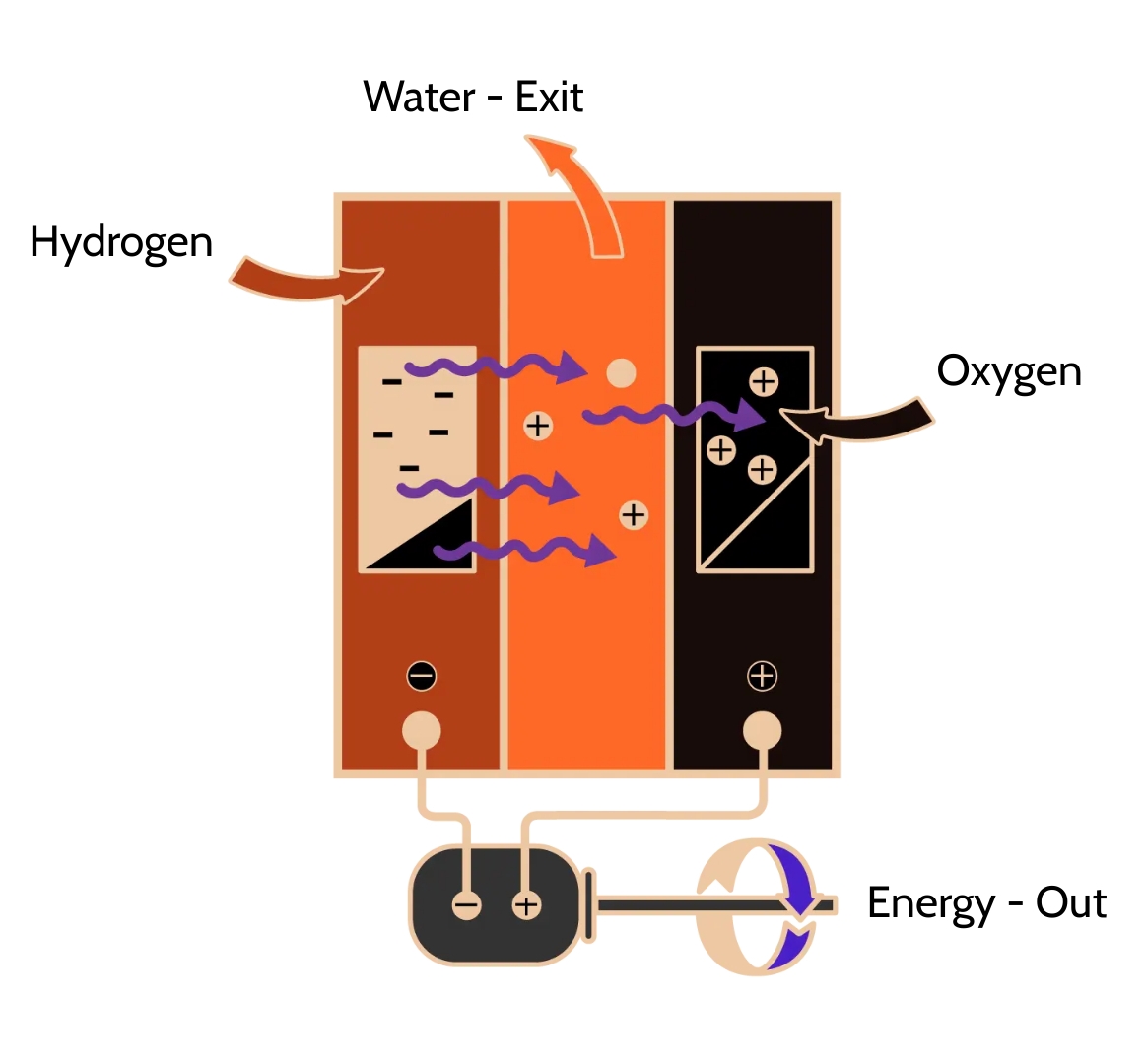
Despite having a wide range of configurations, fuel cells work on the same fundamental principles. However, the reaction rate is quite slow. This problem is solved using a different type of catalyst. The catalyst is properly split before being introduced into the electrodes to maximize the surface area.
Types of fuel cells
Based on their working temperature, efficiency, uses, and price, fuel cells can be classified in a variety of ways. They are divided into six main groups according to the fuel and electrolyte they use.
- Alkaline fuel cell
- Solid oxide fuel cell
- Phosphoric acid fuel cell
- Proton exchange membrane fuel cell
- Molten carbonate fuel cell
- Direct methanol fuel cell
1. Alkaline fuel cell
The alkaline fuel cell uses the KOH in a water-based solution to generate electricity. It is categorized as fuel cells with low temperatures of operation (50 and 95 degrees Celsius) and affordable catalyst. Nickel is the most widely popular catalyst used in this type of fuel cell. Nowadays, they work on boats, submarines, heavy equipment, and other specialized transport equipment.
2. Solid oxide fuel cell
Typically, this technology uses a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide (CO). It is categorized as fuel cells with high temperatures of operation (900-1000 °C) with a novel metallic oxide ceramic electrolyte. They are the most efficient fuel cells, with efficiencies between 50% and 60%. But producing such technologies is still showing to be extremely costly, because stability it requires the pricey high temperature alloys.
3. Phosphoric acid fuel cell
Carbon coated electrodes & liquid H3PO4 electrolyte are used in phosphoric acid fuel cells. Because phosphoric acid has a weak conductivity at relatively low temperature, phosphoric acid fuel cells can function in the 140–240 °C range of temperature. The proton serves as the charge transfer in this kind of fuel cell.
4. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell
They are small, lightweight systems with quick starting times. This system is typically employed in mobile and fixed applications. Due to the lack of moving components in the fuel cell’s power-generating stacks, it also require little maintenance. The proton exchange membrane fuel cell is operated between 45–90°C.
5. Molten carbonate fuel cell
A molten mixture of potassium carbonate & lithium carbonate serves as the electrolyte in molten carbonate fuel cells. They are being used in electricity company, commercial, and defense applications for fossil fuels and coal-based power stations. Molten carbonate fuel cells don’t need any infrastructure to be built to be installed, although it takes some time for them to reach operating temperatures and begin producing power.
6. Direct methanol fuel cell
Proton Exchange Membrane, which offers low penetrability & high proton conductivity, is regarded as the main component of the direct methanol fuel cell. It offers excellent chemical and thermal stability for optimum direct methanol fuel cell performance. They are considered sustainable renewable energy sources that do not require charging.
Applications
Fuel cells can potentially be utilized for any application that requires energy due to its high flexibility, broad energy range, and variety of features among various types. These applications vary from motorcycles to huge co – generation power stations. Some of the fuel cell application are given below.
-
Portable applications
Portable applications typically have power requirements of less than 1 kW. Battery technologies are not appropriate for high-power & long-life portable applications. It is anticipated that fuel cells technologies will soon begin to be replaced primary (disposable) & secondary (rechargeable) batteries in small portable electronics.
-
Transportation applications
Numerous types of vehicles, including cars, buses, commercial vehicles, scooters, & bicycles, can be powered by fuel cells. Companies are interested in fuel cell technology, since it is an “upcoming” technology with the possibility of fuel replication and almost low environmental impact with zero emission.
-
Backup power
When the main power supply is disturbed, backup power systems offer electricity. There are many different sizes & varieties of fuel cells that are utilized as backup power sources, and they typically burn hydrogen. Computer systems, production facilities, residences, and power grids are some application that uses fuel cell for backup generators.
Cite this Article
| Author: | Scholars Harbor |
| Year: | 2022 |
| Title | All about Fuel Cell? – Working, Types & Its Applications Explained |
| Publisher: | Scholars Harbor |
| URL: | https://scholarsharbor.com/all-about-fuel-cell-working-types-its-applications-explained/ |










Discussion about this post